Meet the man behind the myth. Napoleon, directed by Ridley Scott and starring Joaquin Phoenix and Vanessa Kirby, exclusively in theaters now. Directed by Ridley Scott from a screenplay by David Scarpa, “Napoleon” stars Joaquin Phoenix as the French emperor and military leader. The film is an original and personal look at Napoleon’s origins and his swift, ruthless climb to emperor, viewed through the prism of his addictive and often volatile relationship with his wife and one true love, Josephine, played by Vanessa Kirby. The film captures Napoleon’s famous battles, relentless ambition and astounding strategic mind as an extraordinary military leader and war visionary. An Apple Studios production in conjunction with Scott Free Productions, “Napoleon” is produced by Scott, Kevin Walsh, Mark Huffam and Phoenix, with Michael Pruss and Aidan Elliott serving as executive producers.
 |
| Napoleon Bonaparte |
 |
| The Coronation of Joséphine de Beauharnais |


Related Articles
There have been five republics in the history of France:
- French First Republic (1792–1804)
- French Second Republic (1848–1852)
- French Third Republic (1870–1940)
- French Fourth Republic (1946–1958)
- French Fifth Republic (1958–present)
French Revolution: Timeline, Causes & Dates | HISTORY
www.history.com › Topics › European History
History Channel · Nov 9, 2009
History Channel · Nov 9, 2009
3:14 - In 1804, Napoleon Bonaparte declared himself Emperor of the French, under the title Napoleon I. As the architect of France's recovery following the ...
YouTube · History Matters · Sep 12, 2016
History Channel · Jesse Greenspan · Apr 11, 2014
NGV · May 10, 2012
Khan Academy · Aug 26, 2011
7 key moments in this video
NGV · May 11, 2012
The French Renaissance saw spectacular cultural development and the first standardisation of the French language, which would become the official language of France and the language of Europe's aristocracy. It also saw a long set of wars, known as the Italian Wars, between France and the House of Habsburg. French explorers such as Jacques Cartier and Samuel de Champlain claimed lands in the Americas for France, paving the way for the expansion of the French colonial empire. The rise of Protestantism in Europe led France to a civil war known as the French Wars of Religion, where, in the most notorious incident, thousands of Huguenots were murdered in the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre of 1572.[52] The Wars of Religion were ended by Henry IV's Edict of Nantes, which granted some freedom of religion to the Huguenots. Spanish troops, the terror of Western Europe,[53] assisted the Catholic side from 1589 to 1594 and invaded northern France in 1597; after some skirmishing in the 1620s and 1630s, Spain and France returned to all-out war between 1635 and 1659. The war cost France 300,000 casualties.[54]
Under Louis XIII, Cardinal Richelieu promoted the centralisation of the state and reinforced royal power by disarming domestic power holders in the 1620s. He systematically destroyed castles of defiant lords and denounced the use of private violence (duelling, carrying weapons and maintaining private armies). By the end of the 1620s, Richelieu established "the royal monopoly of force" as the doctrine.[55]
From the 16th to the 19th century, France was responsible for 11% of the transatlantic slave trade,[56] second only to Great Britain during the 18th century.[57] While the state began condoning the practice with letters patent in the 1630s, Louis XIII only formalized this authorization more generally in 1642 in the last year of his reign. By the mid-18th century, Nantes had become the principal French slave-trading port.[56]

During Louis XIV's minority and the regency of Queen Anne and Cardinal Mazarin, a period of trouble known as the Fronde occurred in France. This rebellion was driven by the great feudal lords and sovereign courts as a reaction to the rise of royal absolute power in France. The monarchy reached its peak during the 17th century and the reign of Louis XIV. By turning powerful feudal lords into courtiers at the Palace of Versailles, his command of the military went unchallenged. Remembered for numerous wars, the so-called "Sun King" made France the leading European power. France became the most populous country in Europe and had tremendous influence over European politics, economy, and culture. French became the most-used language in diplomacy, science, literature and international affairs, and remained so until the 20th century.[58] During his reign, France took colonial control of many overseas territories in the Americas, Africa and Asia. In 1685, Louis XIV revoked the Edict of Nantes, forcing thousands of Huguenots into exile and published the Code Noir providing the legal framework for slavery and expelling Jewish people from the French colonies.[59]
Under the wars of Louis XV (r. 1715–1774), France lost New France and most of its Indian possessions after its defeat in the Seven Years' War (1756–1763). Its European territory kept growing, however, with notable acquisitions such as Lorraine (1766) and Corsica (1770). An unpopular king, Louis XV's weak rule, his ill-advised financial, political and military decisions—as well as the decadence of his court—discredited the monarchy, which arguably paved the way for the French Revolution 15 years after his death.[60]
Louis XVI (r. 1774–1793) actively supported the Americans with money, fleets and armies, helping them win independence from Great Britain. France gained revenge but spent so heavily that the government verged on bankruptcy—a factor that contributed to the French Revolution. Some of the Enlightenment occurred in French intellectual circles, and major scientific breakthroughs and inventions, such as the naming of oxygen (1778) and the first hot air balloon carrying passengers (1783), were achieved by French scientists. French explorers, such as Bougainville and Lapérouse, took part in the voyages of scientific exploration through maritime expeditions around the globe. The Enlightenment philosophy, in which reason is advocated as the primary source of legitimacy, undermined the power of and support for the monarchy and also was a factor in the French Revolution.
Revolutionary France (1789–1799)

Facing financial troubles, Louis XVI summoned the Estates-General (gathering the three Estates of the realm) in May 1789 to propose solutions to his government. As it came to an impasse, the representatives of the Third Estate formed a National Assembly, signalling the outbreak of the French Revolution. Fearing that the king would suppress the newly created National Assembly, insurgents stormed the Bastille on 14 July 1789, a date which would become France's National Day.
In early August 1789, the National Constituent Assembly abolished the privileges of the nobility such as personal serfdom and exclusive hunting rights. Through the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (27 August 1789), France established fundamental rights for men. The declaration affirms "the natural and imprescriptible rights of man" to "liberty, property, security and resistance to oppression". Freedom of speech and press were declared, and arbitrary arrests were outlawed. It called for the destruction of aristocratic privileges and proclaimed freedom and equal rights for all men, as well as access to public office based on talent rather than birth. In November 1789, the Assembly decided to nationalise and sell all property of the Catholic Church which had been the largest landowner in the country. In July 1790, a Civil Constitution of the Clergy reorganised the French Catholic Church, cancelling the authority of the Church to levy taxes, et cetera. This fueled much discontent in parts of France, which would contribute to the civil war breaking out some years later. While Louis XVI still enjoyed popularity among the population, his disastrous flight to Varennes in June 1791 seemed to justify rumours he had tied his hopes of political salvation to the prospects of foreign invasion. His credibility was so deeply undermined that the abolition of the monarchy and the establishment of a republic became an increasing possibility.
In the August 1791 Declaration of Pillnitz, the Emperor of Austria and the King of Prussia threatened to restore the French monarch by force. In September 1791, the National Constituent Assembly forced Louis XVI to accept the French Constitution of 1791, thus turning the French absolute monarchy into a constitutional monarchy. In the newly established Legislative Assembly (October 1791), enmity developed and deepened between a group later called the 'Girondins', who favoured war with Austria and Prussia, and a group later called 'Montagnards' or 'Jacobins' who opposed such a war. A majority in the Assembly in 1792 however saw a war with Austria and Prussia as a chance to boost the popularity of the revolutionary government and thought that such a war could be won and so declared war on Austria on 20 April 1792.

On 10 August 1792, an angry crowd threatened the palace of Louis XVI, who took refuge in the Legislative Assembly.[61][62] A Prussian army invaded France later in August 1792. In early September, Parisians, infuriated by the Prussian Army capturing Verdun and counter-revolutionary uprisings in the west of France, murdered between 1,000 and 1,500 prisoners by raiding the Parisian prisons. The Assembly and the Paris City Council seemed unable to stop that bloodshed.[61][63] The National Convention, chosen in the first elections under male universal suffrage,[61] on 20 September 1792 succeeded the Legislative Assembly and on 21 September abolished the monarchy by proclaiming the French First Republic. Louis XVI was convicted of treason and guillotined in January 1793. France had declared war on Great Britain and the Dutch Republic in November 1792 and did the same on Spain in March 1793; in the spring of 1793, Austria and Prussia invaded France; in March, France created a "sister republic" in the "Republic of Mainz" and kept it under control.
Also in March 1793, a counter-revolution in Vendée began, evoked by both the Civil Constitution of the Clergy of 1790 and the nationwide army conscription in early 1793; elsewhere in France rebellion was brewing too. A factionalist feud in the National Convention, smouldering ever since October 1791, came to a climax on 2 June 1793 with the group of the Girondins being forced to resign and leave the convention. By July the counter-revolution had spread to Brittany, Normandy, Bordeaux, Marseilles, Toulon, and Lyon. Between October and December 1793, Paris' Convention government took brutal measures to subdue most internal uprisings at the cost of tens of thousands of lives. Some historians consider the civil war to have lasted until 1796 with a toll of possibly 450,000 lives.[64] By the end of 1793, the allies had been driven from France.
Political disagreements and enmity in the National Convention reached unprecedented levels, leading to dozens of Convention members being sentenced to death and guillotined. Meanwhile, France's external wars in 1794 were prospering, for example in Belgium. In 1795, the government seemed to return to indifference towards the desires and needs of the lower classes concerning freedom of (Catholic) religion and fair distribution of food. Until 1799, politicians, apart from inventing a new parliamentary system (the 'Directory'), busied themselves with dissuading the people from Catholicism and royalism.
Napoleon and 19th century (1799–1914)

General Napoleon Bonaparte seized control of the Republic in 1799 becoming First Consul and later Emperor of the French Empire (1804–1814; 1815). As a continuation of the French Revolutionary Wars, changing sets of European coalitions declared wars on Napoleon's empire. His armies conquered most of continental Europe with swift victories such as the battles of Jena-Auerstadt and Austerlitz. Members of the Bonaparte family were appointed as monarchs in some of the newly established kingdoms.[66]
These victories led to the worldwide expansion of French revolutionary ideals and reforms, such as the metric system, the Napoleonic Code and the Declaration of the Rights of Man. In June 1812 Napoleon attacked Russia, reaching Moscow. Thereafter his army disintegrated through supply problems, disease, Russian attacks, and finally winter. After the catastrophic Russian campaign and the ensuing uprising of European monarchies against his rule, Napoleon was defeated. About a million Frenchmen died during the Napoleonic Wars.[66] After his brief return from exile, Napoleon was finally defeated in 1815 at the Battle of Waterloo, and the Bourbon monarchy was restored with new constitutional limitations.
The discredited Bourbon dynasty was overthrown by the July Revolution of 1830, which established the constitutional July Monarchy. In that year, French troops began the conquest of Algeria, establishing the first colonial presence in Africa since Napoleon's abortive invasion of Egypt in 1798. In 1848, general unrest led to the February Revolution and the end of the July Monarchy. The abolition of slavery and the introduction of male universal suffrage, which were briefly enacted during the French Revolution, was re-enacted in 1848. In 1852, the president of the French Republic, Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte, Napoleon I's nephew, was proclaimed emperor of the Second Empire, as Napoleon III. He multiplied French interventions abroad, especially in Crimea, Mexico and Italy which resulted in the annexation of the Duchy of Savoy and the County of Nice, then part of the Kingdom of Sardinia. Napoleon III was unseated following defeat in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870, and his regime was replaced by the Third Republic. By 1875, the French conquest of Algeria was complete, with approximately 825,000 Algerians killed from famine, disease, and violence.[67]
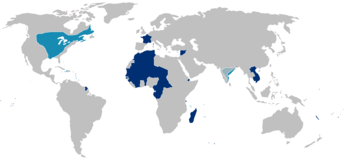
France had colonial possessions, in various forms since the beginning of the 17th century, but in the 19th and 20th centuries its global overseas colonial empire extended greatly and became the second-largest in the world behind the British Empire.[15] Including metropolitan France, the total area of land under French sovereignty reached almost 13 million square kilometres in the 1920s and 1930s, 8.6% of the world's land. Known as the Belle Époque, the turn of the century was a period characterised by optimism, regional peace, economic prosperity and technological, scientific and cultural innovations. In 1905, state secularism was officially established.






