History of religion
| Part of a series on |
| History of religions |
|---|
The history of religion refers to the written record of human religious feelings, thoughts, and ideas. This period of religious history begins with the invention of writing about 5,200 years ago (3200 BCE).[1] The prehistory of religion involves the study of religious beliefs that existed prior to the advent of written records. One can also study comparative religious chronology through a timeline of religion. Writing played a major role in standardizing religious texts regardless of time or location, and making easier the memorization of prayers and divine rules. A small part of the Bible involves the collation of oral texts handed down over the centuries.[2]
The concept of "religion" was formed in the 16th and 17th centuries.[3][4] Sacred texts like the Bible, the Quran, and others did not have a word or even a concept of religion in the original languages and neither did the people or the cultures in which these sacred texts were written.[5][6]
The word religion as used in the 21st century does not have an obvious pre-colonial translation into non-European languages. The anthropologist Daniel Dubuisson writes that "what the West and the history of religions in its wake have objectified under the name 'religion' is ... something quite unique, which could be appropriate only to itself and its own history".[7] The history of other cultures' interaction with the "religious" category is therefore their interaction with an idea that first developed in Europe under the influence of Christianity.[8]
History of study
The school of religious history called the Religionsgeschichtliche Schule, a late 19th-century German school of thought, originated the systematic study of religion as a socio-cultural phenomenon. It depicted religion as evolving with human culture, from polytheism to monotheism.
The Religionsgeschichtliche Schule emerged at a time when scholarly study of the Bible and of church history flourished in Germany and elsewhere (see higher criticism, also called the historical-critical method). The study of religion is important: religion and similar concepts have often shaped civilizations' law and moral codes, social structure, art and music.
Origin
The earliest archeological evidence interpreted by some as suggestive of the emergence of religious ideas dates back several hundred thousand years, to the Middle and Lower Paleolithic periods: some archaeologists conclude that the apparently intentional burial of early Homo sapiens and Neanderthals and even Homo naledi as early as 300,000 years ago is proof that religious ideas already existed, but such a connection is entirely conjectural. Other evidence that some infer as indicative of religious ideas includes symbolic artifacts from Middle Stone Age sites in Africa. However, the interpretation of early paleolithic artifacts, with regard to how they relate to religious ideas, remains controversial. Archeological evidence from more recent periods is less controversial. Scientists[which?] generally interpret a number of artifacts from the Upper Paleolithic (50,000–13,000 BCE) as representing religious ideas. Examples of Upper Paleolithic remains that some associate with religious beliefs include the lion man, the Venus figurines, and the elaborate ritual burial from Sungir.
In the 19th century, researchers proposed various theories regarding the origin of religion, challenging earlier claims of a Christianity-like urreligion. Early theorists, such as Edward Burnett Tylor (1832–1917) and Herbert Spencer (1820–1903), emphasized the concept of animism, while archaeologist John Lubbock (1834–1913) used the term "fetishism". Meanwhile, the religious scholar Max Müller (1823–1900) theorized that religion began in hedonism and the folklorist Wilhelm Mannhardt (1831–1880) suggested that religion began in "naturalism" – by which he meant mythological explanations for natural events.[9][page needed] All of these theories have been widely criticized since then; there is no broad consensus regarding the origin of religion.
Pre-pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) Göbekli Tepe, the oldest potentially religious site yet discovered anywhere[10] includes circles of erected massive T-shaped stone pillars, the world's oldest known megaliths[11] decorated with abstract, enigmatic pictograms and carved-animal reliefs. The site, near the home place of original wild wheat, was built before the so-called Neolithic Revolution, i.e., the beginning of agriculture and animal husbandry around 9000 BCE. But the construction of Göbekli Tepe implies organization of an advanced order not hitherto associated with Paleolithic, PPNA, or PPNB societies. The site, abandoned around the time the first agricultural societies started, is still being excavated and analyzed, and thus might shed light on the significance it had, if any, for the religions of older, foraging communities, as well as for the general history of religions.
The Pyramid Texts from ancient Egypt, the oldest known religious texts in the world, date to between 2400 and 2300 BCE.[12][13]
The earliest records of Indian religion are the Vedas, composed c. 1500–1200 BCE during the Vedic Period.
Surviving early copies of religious texts include:
- The Upanishads, some of which date to the mid-first millennium BCE.
- The Dead Sea Scrolls, representing fragmentary texts of the Hebrew Tanakh.[14]
- Complete Hebrew texts, also of the Tanakh, but translated into the Greek language (Septuagint 300–200 BCE), were in wide use by the early 1st century CE.
- The Zoroastrian Avesta, from a Sassanian-era master copy.
Axial age
Some historians have labelled the period from 900 to 200 BCE as the "axial age", a term coined by German-Swiss philosopher Karl Jaspers (1883–1969). According to Jaspers, in this era of history "the spiritual foundations of humanity were laid simultaneously and independently... And these are the foundations upon which humanity still subsists today." Intellectual historian Peter Watson has summarized this period as the foundation time of many of humanity's most influential philosophical traditions, including monotheism in Persia and Canaan, Platonism in Greece, Buddhism and Jainism in India, and Confucianism and Taoism in China. These ideas would become institutionalized in time – note for example Ashoka's role in the spread of Buddhism, or the role of Neoplatonic philosophy in Christianity at its foundation.
The historical roots of Jainism in India date back to the 9th century BCE with the rise of Parshvanatha and his non-violent philosophy.[15][16][need quotation to verify]
Middle Ages
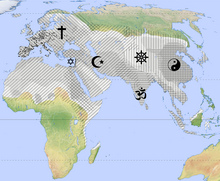
World religions of the present day established themselves throughout Eurasia during the Middle Ages by:
- Christianization of the Western world
- Buddhist missions to East Asia
- the decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent
- the spread of Islam throughout the Middle East, Central Asia, North Africa and parts of Europe and India
During the Middle Ages, Muslims came into conflict with Zoroastrians during the Muslim conquest of Persia (633–654); Christians fought against Muslims during the Arab–Byzantine wars (7th to 11th centuries), the Crusades (1095 onward), the Reconquista (718–1492), the Ottoman wars in Europe (13th century onwards) and the Inquisition; Shamanism was in conflict with Buddhists, Taoists, Muslims and Christians during the Mongol invasions and conquests (1206–1337); and Muslims clashed with Hindus and Sikhs during the Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent (8th to 16th centuries).
Many medieval religious movements continued to emphasize mysticism, such as the Cathars and related movements in the West, the Jews in Spain (see Zohar), the Bhakti movement in India and Sufism in Islam. Monotheism and related mysticisms reached definite forms in Christian Christology and in Islamic Tawhid. Hindu monotheist notions of Brahman likewise reached their classical form with the teaching of Adi Shankara (788–820).
Modern Ages
From the 15th century to the 19th century, European colonisation resulted in the spread of Christianity to Sub-Saharan Africa, and the Americas, Australia and the Philippines. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century played a major role in the rapid spread of the Protestant Reformation under leaders such as Martin Luther (1483–1546) and John Calvin (1509–1564). Wars of religion broke out, culminating in the Thirty Years' War which ravaged Central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The 18th century saw the beginning of secularisation in Europe, a trend which gained momentum after the French Revolution broke out in 1789. By the late 20th century, religion had declined in most of Europe.[17]
See also
- Growth of religion
- Historiography of religion
- Religion and politics
- Christianity and politics
- Judaism and politics
- Political aspects of Islam
- Women and religion
- Women as theological figures
- List of founders of religious traditions
- List of religions and spiritual traditions
- List of religious movements that began in the United States
Shamanism and ancestor worship
Panentheism
Polytheism
References
Citations
- ^ "The Origins of Writing | Essay | Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History | The Metropolitan Museum of Art". Metmuseum.org. Retrieved 2018-03-11.
- ^ Humayun Ansari (2004). The Infidel Within: Muslims in Britain Since 1800. C. Hurst & Co. pp. 399–400. ISBN 978-1-85065-685-2.
- ^ Nongbri, Brent (2013). Before Religion: A History of a Modern Concept. Yale University Press. p. 152. ISBN 978-0300154160.
Although the Greeks, Romans, Mesopotamians, and many other peoples have long histories, the stories of their respective religions are of recent pedigree. The formation of ancient religions as objects of study coincided with the formation of religion itself as a concept of the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.
- ^ Harrison, Peter (1990). 'Religion' and the Religions in the English Enlightenment. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 1. ISBN 978-0521892933.
That there exist in the world such entities as 'the religions' is an uncontroversial claim...However, it was not always so. The concepts 'religion' and 'the religions', as we presently understand them, emerged quite late in Western thought, during the Enlightenment. Between them, these two notions provided a new framework for classifying particular aspects of human life.
- ^ Nongbri, Brent (2013). "2. Lost in Translation: Inserting "Religion" into Ancient Texts". Before Religion: A History of a Modern Concept. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0300154160.
- ^ Morreall, John; Sonn, Tamara (2013). 50 Great Myths about Religions. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 13. ISBN 9780470673508.
Many languages do not even have a word equivalent to our word 'religion'; nor is such a word found in either the Bible or the Qur'an.
- ^ Daniel Dubuisson. The Western Construction of Religion. 1998. William Sayers (trans.) Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2003. p. 90.
- ^ Timothy Fitzgerald. Discourse on Civility and Barbarity. ISBN 9780190293642. Oxford University Press, 2007. pp.45-46.
- ^ "Religion". Encyclopedia Universal Ilustrada Europeo-Americana, 70 vols. Madrid. 1907-1930.
- ^ "The World's First Temple". Archaeology magazine. Nov–Dec 2008. p. 23.
- ^ Sagona, Claudia (25 August 2015). The Archaeology of Malta. Cambridge University Press. p. 47. ISBN 9781107006690. Retrieved 25 November 2016.
- ^ Budge, Wallis (January 1997). An Introduction to Ancient Egyptian Literature. p. 9. ISBN 0-486-29502-8.
- ^ Allen, James (2005). The Ancient Egyptian Pyramid Texts. ISBN 1-58983-182-9.
- ^ Abegg, Martin G.; Flint, Peter; Ulrich, Eugene (1999). The Dead Sea Scrolls Bible: The Oldest Known Bible Translated for the First Time into English. Harper Collins (published 2012). p. xvii. ISBN 9780062031129. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
The Dead Sea Scrolls include more than 225 'biblical' manuscripts [...]. Unfortunately, with a few exceptions [...] almost all these manuscripts are in fragmentary form. Parts of every book of the Jewish and Protestant Old Testament are included, with the exception of Esther and Nehemiah.
- ^ Dundas 2002, p. 30.
- ^ Zimmer 1953, p. 182-183.
- ^ Norris, Pippa (2011). Sacred and Secular: Religion and Politics Worldwide. Cambridge University Press.
Sources
- Dundas, Paul (2002) [1992], The Jains (Second ed.), London and New York: Routledge, ISBN 0-415-26605-X
- Stausberg, Michael (March 2021). Feldt, Laura; Valk, Ülo (eds.). "The Demise, Dissolution, and Elimination of Religions". Numen. Leiden and Boston: Brill Publishers. 68 (2–3 - Special Issue: The Dissolution of Religions): 103–131. doi:10.1163/15685276-12341617. ISSN 1568-5276. LCCN 58046229.
- Zimmer, Heinrich (1953) [April 1952], Campbell, Joseph (ed.), Philosophies Of India, London: Routledge & Kegan Paul Ltd., ISBN 978-81-208-0739-6
Further reading
- Armstrong, Karen. A History of God: The 4,000-Year Quest of Judaism, Christianity and Islam (1994) excerpt and text search
- Armstrong, Karen. Islam: A Short History (2002) excerpt and text search
- Bowker, John Westerdale, ed. The Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (2007) excerpt and text search 1126pp
- Carus, Paul. The history of the devil and the idea of evil: from the earliest times to the present day (1899) full text
- Eliade, Mircea, and Joan P. Culianu. The HarperCollins Concise Guide to World Religion: The A-to-Z Encyclopedia of All the Major Religious Traditions (1999) covers 33 principal religions, including Buddhism, Christianity, Jainism, Judaism, Islam, Shinto, Shamanism, Taoism, South American religions, Baltic and Slavic religions, Confucianism, and the religions of Africa and Oceania.
- Eliade, Mircea ed. Encyclopedia of Religion (16 vol. 1986; 2nd ed 15 vol. 2005; online at Gale Virtual Reference Library). 3300 articles in 15,000 pages by 2000 experts.
- Ellwood, Robert S. and Gregory D. Alles. The Encyclopedia of World Religions (2007), p 528; for middle schools
- Gilley, Sheridan; Shiels, W. J. History of Religion in Britain: Practice and Belief from Pre-Roman Times to the Present (1994), p. 590.
- James, Paul; Mandaville, Peter (2010). Globalization and Culture, Vol. 2: Globalizing Religions. London: Sage Publications.
- Marshall, Peter. "(Re)defining the English Reformation," Journal of British Studies, July 2009, Vol. 48#3 pp 564–586
- Rüpke, Jörg, Religion, EGO – European History Online, Mainz: Institute of European History, 2020, retrieved: March 8, 2021.
- Schultz, Kevin M.; Harvey, Paul. "Everywhere and Nowhere: Recent Trends in American Religious History and Historiography," Journal of the American Academy of Religion, March 2010, Vol. 78#1 pp. 129–162
- Wilson, John F. Religion and the American Nation: Historiography and History (2003) p. 119.
External links
- Historyofreligions.com
- The history of religious and philosophical ideas, in Dictionary of the History of Ideas
- History of Religion as flash animation
- The history and origins of world religions depicted as a navigable tree
