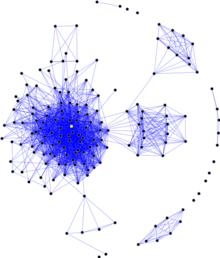
| Sociology |
|---|
 A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactionsbetween actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities as well as a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures.[1] The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine network dynamics. A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactionsbetween actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities as well as a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures.[1] The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine network dynamics. |
Social networks and the analysis of them is an inherently
interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from
socialpsychology,
sociology,
statistics, and
graph theory.
Georg Simmel authored early structural theories in sociology emphasizing the dynamics of triads and "web of group affiliations".
[2] Jacob Moreno is credited with developing the first
sociograms in the 1930s to study interpersonal relationships. These approaches were mathematically formalized in the 1950s and theories and methods of social networks became pervasive in the social and behavioral sciences by the 1980s.
[1][3] Social network analysis is now one of the major paradigms in contemporary sociology, and is also employed in a number of other social and formal sciences. Together with other
complex networks, it forms part of the nascent field of
network science.
[4][5]
Overview
The social network is a
theoretical construct useful in the
social sciences to study relationships between individuals,
groups,
organizations, or even entire
societies (
social units, see
differentiation). The term is used to describe a
social structure determined by such
interactions. The ties through which any given social unit connects represent the convergence of the various social contacts of that unit. This theoretical approach is, necessarily, relational. An
axiom of the social network approach to understanding
social interaction is that social phenomena should be primarily conceived and investigated through the properties of relations between and within units, instead of the properties of these units themselves. Thus, one common criticism of social network theory is that
individual agency is often ignored
[6] although this may not be the case in practice (see
agent-based modeling). Precisely because many different types of relations, singular or in combination, form these network configurations,
network analytics are useful to a broad range of research enterprises. In social science, these fields of study include, but are not limited to
anthropology,
biology,
communication studies,
economics,
geography,
information science,
organizational studies,
social psychology,
sociology, and
sociolinguistics.
History
In the late 1890s, both
Émile Durkheim and
Ferdinand Tönnies foreshadowed the idea of social networks in their theories and research of
social groups. Tönnies argued that social groups can exist as personal and direct social ties that either link individuals who share values and belief (
Gemeinschaft, German, commonly translated as "
community") or impersonal, formal, and instrumental social links (
Gesellschaft, German, commonly translated as "
society").
[7] Durkheim gave a non-individualistic explanation of social facts, arguing that social phenomena arise when interacting individuals constitute a reality that can no longer be accounted for in terms of the properties of individual actors.
[8] Georg Simmel, writing at the turn of the twentieth century, pointed to the nature of networks and the effect of network size on interaction and examined the likelihood of interaction in loosely knit networks rather than groups.
[9]
Moreno's sociogram of a 2nd grade class
Major developments in the field can be seen in the 1930s by several groups in psychology, anthropology, and mathematics working independently.
[6][10][11] In
psychology, in the 1930s,
Jacob L. Moreno began systematic recording and analysis of social interaction in small groups, especially classrooms and work groups (see
sociometry). In
anthropology, the foundation for social network theory is the theoretical and
ethnographic work of
Bronislaw Malinowski,
[12] Alfred Radcliffe-Brown,
[13][14] and
Claude Lévi-Strauss.
[15] A group of social anthropologists associated with
Max Gluckman and the
Manchester School, including
John A. Barnes,
[16] J. Clyde Mitchell and
Elizabeth Bott Spillius,
[17][18] often are credited with performing some of the first fieldwork from which network analyses were performed, investigating community networks in southern Africa, India and the United Kingdom.
[6] Concomitantly, British anthropologist
S. F. Nadel codified a theory of social structure that was influential in later network analysis.
[19] In
sociology, the early (1930s) work of
Talcott Parsons set the stage for taking a relational approach to understanding social structure.
[20][21] Later, drawing upon Parsons' theory, the work of sociologist
Peter Blau provides a strong impetus for analyzing the relational ties of social units with his work on
social exchange theory.
[22][23][24]
Beginning in the late 1990s, social network analysis experienced work by sociologists, political scientists, and physicists such as
Duncan J. Watts,
Albert-László Barabási,
Peter Bearman,
Nicholas A. Christakis,
James H. Fowler, and others, developing and applying new models and methods to emerging data available about online social networks, as well as "digital traces" regarding face-to-face networks.
Levels of analysis
Self-organization of a network, based on Nagler, Levina, & Timme, (2011)[31]
In general, social networks are
self-organizing,
emergent, and
complex, such that a globally coherent pattern appears from the local interaction of the elements that make up the system.
[32][33] These patterns become more apparent as network size increases. However, a global network analysis
[34] of, for example, all
interpersonal relationships in the world is not feasible and is likely to contain so much
information as to be uninformative. Practical limitations of computing power, ethics and participant recruitment and payment also limit the scope of a social network analysis.
[35][36] The nuances of a local system may be lost in a large network analysis, hence the quality of information may be more important than its scale for understanding network properties. Thus, social networks are analyzed at the scale relevant to the researcher's theoretical question. Although
levels of analysis are not necessarily
mutually exclusive, there are three general levels into which networks may fall:
micro-level,
meso-level, and
macro-level.
Micro level
At the micro-level, social network research typically begins with an individual,
snowballing as social relationships are traced, or may begin with a small group of individuals in a particular social context.
Triadic level: Add one individual to a dyad, and you have a
triad. Research at this level may concentrate on factors such as
balance and
transitivity, as well as
social equality and tendencies toward
reciprocity/mutuality.
[35] In the
balance theory of
Fritz Heider the triad is the key to social dynamics. The discord in a rivalrous
love triangle is an example of an unbalanced triad, likely to change to a balanced triad by a change in one of the relations. The dynamics of social friendships in society has been modeled by balancing triads. The study is carried forward with the theory of
signed graphs.
Actor level: The smallest unit of analysis in a social network is an individual in their social setting, i.e., an "actor" or "ego". Egonetwork analysis focuses on network characteristics such as size, relationship strength, density,
centrality,
prestige and roles such as
isolates, liaisons, and
bridges.
[37] Such analyses, are most commonly used in the fields of
psychology or
social psychology,
ethnographic kinship analysis or other
genealogical studies of relationships between individuals.
Meso level
In general, meso-level theories begin with a
population size that falls between the micro- and macro-levels. However, meso-level may also refer to analyses that are specifically designed to reveal connections between micro- and macro-levels. Meso-level networks are low density and may exhibit causal processes distinct from interpersonal micro-level networks.
[39]
Social network diagram, meso-level
Organizations: Formal
organizations are
social groups that distribute tasks for a collective
goal.
[40] Network research on organizations may focus on either intra-organizational or inter-organizational ties in terms of
formal or
informal relationships. Intra-organizational networks themselves often contain multiple levels of analysis, especially in larger organizations with multiple branches, franchises or semi-autonomous departments. In these cases, research is often conducted at a workgroup level and organization level, focusing on the interplay between the two structures.
[40] Experiments with networked groups online have documented ways to optimize group-level coordination through diverse interventions, including the addition of autonomous agents to the groups.
[41]
Randomly distributed networks:
Exponential random graph models of social networks became state-of-the-art methods of social network analysis in the 1980s. This framework has the capacity to represent social-structural effects commonly observed in many human social networks, including general
degree-based structural effects commonly observed in many human social networks as well as
reciprocity and
transitivity, and at the node-level,
homophily and
attribute-based activity and popularity effects, as derived from explicit hypotheses about
dependencies among network ties.
Parameters are given in terms of the prevalence of small
subgraph configurations in the network and can be interpreted as describing the combinations of local social processes from which a given network emerges. These probability models for networks on a given set of actors allow generalization beyond the restrictive dyadic independence assumption of micro-networks, allowing models to be built from theoretical structural foundations of social behavior.
[42]
Examples of a random network and a scale-free network. Each graph has 32 nodes and 32 links. Note the "hubs" (shaded) in the scale-free diagram (on the right).
Scale-free networks: A
scale-free network is a
network whose
degree distribution follows a
power law, at least
asymptotically. In
network theory a scale-free ideal network is a
random network with a
degree distribution that unravels the size distribution of social groups.
[43] Specific characteristics of scale-free networks vary with the theories and analytical tools used to create them, however, in general, scale-free networks have some common characteristics. One notable characteristic in a scale-free network is the relative commonness of
vertices with a
degree that greatly exceeds the average. The highest-degree nodes are often called "hubs", and may serve specific purposes in their networks, although this depends greatly on the social context. Another general characteristic of scale-free networks is the
clustering coefficientdistribution, which decreases as the node degree increases. This distribution also follows a
power law.
[44] The
Barabási model of network evolution shown above is an example of a scale-free network.
Macro level
Rather than tracing interpersonal interactions, macro-level analyses generally trace the outcomes of interactions, such as
economic or other
resource transferinteractions over a large
population.
Diagram: section of a large-scale social network
Complex networks: Most larger social networks display features of
social complexity, which involves substantial non-trivial features of
network topology, with patterns of complex connections between elements that are neither purely regular nor purely random (see,
complexity science,
dynamical system and
chaos theory), as do
biological, and
technological networks. Such
complex network features include a heavy tail in the
degree distribution, a high
clustering coefficient,
assortativity or disassortativity among vertices,
community structure (see
stochastic block model), and
hierarchical structure. In the case of
agency-directed networks these features also include
reciprocity, triad significance profile (TSP, see
network motif), and other features. In contrast, many of the mathematical models of networks that have been studied in the past, such as
lattices and
random graphs, do not show these features.
[45]
Theoretical links
Imported theories
Indigenous theories
Few complete theories have been produced from social network analysis. Two that have are
Structural Role Theory and Heterophily Theory.
The basis of Heterophily Theory was the finding in one study that more numerous weak ties can be important in seeking information and innovation, as cliques have a tendency to have more homogeneous opinions as well as share many common traits. This homophilic tendency was the reason for the members of the cliques to be attracted together in the first place. However, being similar, each member of the clique would also know more or less what the other members knew. To find new information or insights, members of the clique will have to look beyond the clique to its other friends and acquaintances. This is what Granovetter called "the strength of weak ties".
[47]
Structural holes
In the context of networks,
social capital exists where people have an advantage because of their location in a network. Contacts in a network provide information, opportunities and perspectives that can be beneficial to the central player in the network. Most social structures tend to be characterized by dense clusters of strong connections.
[48] Information within these clusters tends to be rather homogeneous and redundant. Non-redundant information is most often obtained through contacts in different clusters.
[49] When two separate clusters possess non-redundant information, there is said to be a structural hole between them.
[49] Thus, a network that bridges
structural holes will provide network benefits that are in some degree additive, rather than overlapping. An ideal network structure has a vine and cluster structure, providing access to many different clusters and structural holes.
[49]
Networks rich in structural holes are a form of social capital in that they offer
information benefits. The main player in a network that bridges structural holes is able to access information from diverse sources and clusters.
[49] For example, in
business networks, this is beneficial to an individual's career because he is more likely to hear of job openings and opportunities if his network spans a wide range of contacts in different industries/sectors. This concept is similar to Mark Granovetter's theory of
weak ties, which rests on the basis that having a broad range of contacts is most effective for job attainment.
Research clusters
Communication
Communication Studies are often considered a part of both the social sciences and the humanities, drawing heavily on fields such as
sociology,
psychology,
anthropology,
information science,
biology,
political science, and
economics as well as
rhetoric,
literary studies, and
semiotics. Many communication concepts describe the transfer of information from one source to another, and can thus be conceived of in terms of a network.
In J.A. Barnes' day, a "
community" referred to a specific geographic location and studies of community ties had to do with who talked, associated, traded, and attended church with whom. Today, however, there are extended "online" communities developed through
telecommunications devices and
social network services. Such devices and services require extensive and ongoing maintenance and analysis, often using
network science methods.
Community development studies, today, also make extensive use of such methods.
Complex networks
Criminal networks
In
criminology and
urban sociology, much attention has been paid to the social networks among criminal actors. For example, Andrew Papachristos
[50] has studied gang murders as a series of exchanges between gangs. Murders can be seen to diffuse outwards from a single source, because weaker gangs cannot afford to kill members of stronger gangs in retaliation, but must commit other violent acts to maintain their reputation for strength.
Diffusion of innovations
Diffusion of ideas and innovations studies focus on the spread and use of ideas from one actor to another or one
culture and another. This line of research seeks to explain why some become "early adopters" of ideas and innovations, and links social network structure with facilitating or impeding the spread of an innovation.
Demography
In
demography, the study of social networks has led to new sampling methods for estimating and reaching populations that are hard to enumerate (for example, homeless people or intravenous drug users.) For example, respondent driven sampling is a network-based sampling technique that relies on respondents to a survey recommending further respondents.
Economic sociology
The field of
sociology focuses almost entirely on networks of outcomes of social interactions. More narrowly,
economic sociology considers behavioral interactions of individuals and groups through
social capital and social "markets". Sociologists, such as Mark Granovetter, have developed core principles about the interactions of social structure, information, ability to punish or reward, and trust that frequently recur in their analyses of political, economic and other institutions. Granovetter examines how social structures and social networks can affect economic outcomes like hiring, price, productivity and innovation and describes sociologists' contributions to analyzing the impact of social structure and networks on the economy.
[51]
Health care
Human ecology
Language and linguistics
Literary networks
In the study of literary systems, network analysis has been applied by Anheier, Gerhards and Romo,
[55] De Nooy,
[56] and Senekal,
[57] to study various aspects of how literature functions. The basic premise is that polysystem theory, which has been around since the writings of
Even-Zohar, can be integrated with network theory and the relationships between different actors in the literary network, e.g. writers, critics, publishers, literary histories, etc., can be mapped using
visualization from SNA.
Organizational studies
Social capital
Social capital is a sociological concept about the value of
social relations and the role of cooperation and confidence to achieve positive outcomes. The term refers to the value one can get from their social ties. For example, newly arrived immigrants can make use of their social ties to established migrants to acquire jobs they may otherwise have trouble getting (e.g., because of unfamiliarity with the local language). Studies show that a positive relationship exists between social capital and the intensity of social network use.
[61][62]
Mobility benefits
In many
organizations, members tend to focus their activities inside their own groups, which stifles creativity and restricts opportunities. A player whose network bridges structural holes has an advantage in detecting and developing rewarding opportunities.
[48] Such a player can mobilize social capital by acting as a "broker" of information between two clusters that otherwise would not have been in contact, thus providing access to new ideas, opinions and opportunities. British philosopher and political economist
John Stuart Mill, writes, "it is hardly possible to overrate the value ... of placing human beings in contact with persons dissimilar to themselves.... Such communication [is] one of the primary sources of progress."
[63] Thus, a player with a network rich in structural holes can add value to an organization through new ideas and opportunities. This in turn, helps an individual's career development and advancement.
A social capital broker also reaps control benefits of being the facilitator of information flow between contacts. In the case of consulting firm Eden McCallum, the founders were able to advance their careers by bridging their connections with former big 3 consulting firm consultants and mid-size industry firms.
[64] By bridging structural holes and mobilizing social capital, players can advance their careers by executing new opportunities between contacts.
There has been research that both substantiates and refutes the benefits of information brokerage. A study of high tech Chinese firms by Zhixing Xiao found that the control benefits of structural holes are "dissonant to the dominant firm-wide spirit of cooperation and the information benefits cannot materialize due to the communal sharing values" of such organizations.
[65] However, this study only analyzed Chinese firms, which tend to have strong communal sharing values. Information and control benefits of structural holes are still valuable in firms that are not quite as inclusive and cooperative on the firm-wide level. In 2004, Ronald Burt studied 673 managers who ran the supply chain for one of America's largest electronics companies. He found that managers who often discussed issues with other groups were better paid, received more positive job evaluations and were more likely to be promoted.
[48] Thus, bridging structural holes can be beneficial to an organization, and in turn, to an individual's career.
Social media
Computer networks combined with social networking software produces a new medium for social interaction. A relationship over a computerized
social networking service can be characterized by context, direction, and strength. The content of a relation refers to the resource that is exchanged. In a
computer mediated communication context, social pairs exchange different kinds of information, including sending a data file or a computer program as well as providing emotional support or arranging a meeting. With the rise of
electronic commerce, information exchanged may also correspond to exchanges of money, goods or services in the "real" world.
[66] Social network analysis methods have become essential to examining these types of computer mediated communication.
In addition, the sheer size and the volatile nature of social media has given rise to new network metrics. A key concern with networks extracted from social media is the lack of robustness of network metrics given missing data.
[67]